- Kickigai Weekly
- Posts
- 19 Biases that Affect Your Startup Career
19 Biases that Affect Your Startup Career
Understanding the Subtle Influences Behind Your Career Decisions
Choosing the next step of our career is never an easy task and it’s easy to get influenced by signals of success, rather than what’s best for us.
The most dangerous situation is when we ignore the many biases that drive our career decisions beneath the surface of logic and experience.
By the end of this article, you should be able to recognize your inner biases when evaluating different options (especially startups) to make better, more objective decisions.
Biases when making career decisions
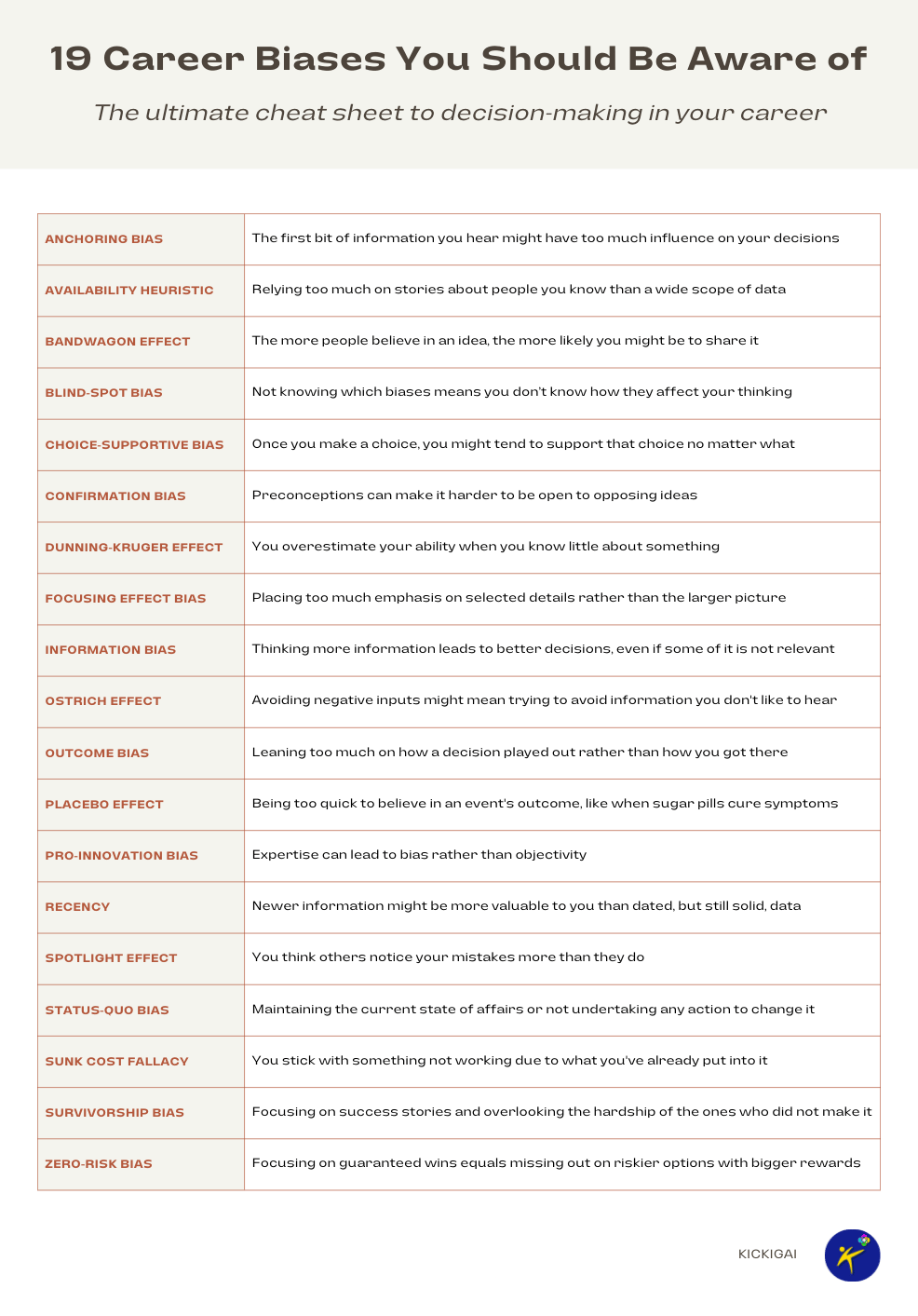
1. Anchoring bias
Definition: The first bit of information you hear might have too much influence on your decisions.
Scenario: After reading about a startup on TechCrunch (or in any other publication) you tend to assume that the company is a synonym of success.
2. Availability heuristic
Definition: Keep referencing anecdotal information?! You might be relying too much on stories about people you know than a wide scope of data
Scenario: An acquaintance of yours is sick and tired of their job at a big company and you assume all roles at big companies suck. The same is true for people you know who had toxic experiences at startups.
3. Bandwagon effect
Definition: The more people believe in an idea, the more likely you might be to share it.
Scenario: If you are surrounded by ambitious people who dream of working in cutting-edge startups, you will end up dreaming about the same future.
4. Blind-spot bias
Definition: If you don't know which biases you have, you might not know how they affect your thinking (aka unknown unknowns)
Scenario: If you were not reading this article, you might never known the subtle triggers and biases behind your decisions
5. Choice-supportive bias
Definition: Once you make a choice, you might tend to support that choice no matter what.
Scenario: After choosing to join a promising startup, you will defend your decision even in the face of new evidence that it was not the right choice.
6. Confirmation bias
Definition: Preconceptions can make it harder to be open to opposing ideas.
Scenario: If you already believe the best companies are the ones that offer job security, benefits and a good work-life balance, you are not going to turn such an offer down, no matter what.
7. Dunning-Kruger Effect
Definition: You overestimate your ability when you know little about something.
Scenario: You have just learned about the basics of sales and negotiation so you believe you’d be great at closing multi-million dollar deals and you should get a senior commercial role at your next company.
8. Focusing Effect Bias
Definition: Placing too much emphasis on a selected detail rather than considering the larger picture. This leads to errors in predicting a future outcome.
Scenario: Working hard for a 5% raise in your current job or playing politics to move to another department within the same company, instead of taking a step back to consider if these options will bring you closer to your goals at all.
9. Information bias
Definition: You might think having lots and lots of information makes for a better decision, even though some of it might not be relevant.
Scenario: Constantly researching and gathering new information before making a decision might lead you to a state of “analysis paralysis”, with each new piece of information being superfluous.
10. Ostrich effect
Definition: Do you avoid negative input? You might be avoiding information you don't like to hear.
Scenario: Someone tells you that you’re wasting your life in your current role but you don’t pay too much attention because if you did, you’d have to question many beliefs and prior decisions.
11. Outcome bias
Definition: You might lean too much on how a decision played out rather than how you arrived at that decision. Good decisions can lead to poor outcomes.
Scenario: A startup that looked great on the surface turns out to be a toxic environment and a sinking ship. You conclude that your decision was wrong but instead, it was the right decision with the information you had at that time.
12. Placebo effect
Definition: You might be too quick to believe in an event's outcome, similar to how a person taking a sugar pill is convinced it will help their headache.
Scenario: You get a job offer after only 2 interviews and you believe it’s because they are acknowledging your potential, instead of other reasons within the company that you can’t know.
13. Pro-innovation bias
Definition: If you invented or are an expert in something, you might be too biased toward it to have an objective opinion.
Scenario: After years of research into a specific field, you are absolutely convinced that the next breakthrough innovation is coming from your field.
14. Recency
Definition: Newer information might be more valuable to you than dated, but still solid, data.
Scenario: A company you want to join has laid off 100s of employees and has reported financial struggles. After a few weeks, they announce a strategic partnership to foster growth so you start believing things are getting better
15. Spotlight Effect
Definition: You think others notice your mistakes or appearance more than they do.
Scenario: You are afraid a bad career choice would ruin your CV forever and everybody would immediately spot your catastrophic mistake.
16. Status-Quo Bias
Definition: Preferring to maintain the current state of affairs or not undertake any action to change it.
Scenario: You delay considering alternative career options and keep postponing making a decision, justifying it by being busy and not having time to think about your career.
17. Sunk Cost Fallacy
Definition: You stick with something not working as well as you expected due to what you've already put into it.
Scenario: You overestimate the risk of leaving your current job or pivoting to a different industry because of all the years you’ve already dedicated to that.
18. Survivorship bias
Definition: When you focus on success stories, you might miss the hardship of the ones who tried the same things but did not succeed.
Scenario: A friend of yours has become successful after joining a startup so this is what you should do. Instead, there are 1000s of equally talented people who also joined startups but did not end up being successful.
19. Zero-risk bias
Definition: Don't want to take a chance? Focusing on goals that guarantee success means you miss out on riskier propositions that could pay off in the end.
Scenario: Joining a large company for a steady job has the opportunity cost of not taking a chance on a rising startup or launching your own company.
Amongst the many cognitive biases out there, these are the ones I observed the most and I hope this list helps you recognize them in yourself and others.
This week's top scientific reads
High temperatures caused 70k deaths in 2022 (The Lancet)
Hearing damage leads to dementia (Journal of Alzheimer's Disease)
The genes behind the shape of human heads (Nature Communications)
Multimodal Foundation Models (ArXiv)
Breakthrough in bladder cancer research (The New England Journal of Medicine)
Read my comments on these articles here.
Latest European funding rounds in health & bio
Ready to turn this news into your next career opportunity? Here is how
Lilio Health raised €2.2M for a baby sensor bracelet that records the most important well-being signals and sends them to parents 🇩🇪
VectorY closed a $137M Series A round for their antibody therapeutics treatment against neurodegenerative diseases 🇳🇱
Solar Foods raised $8M for their new natural protein for the global food industry, produced only from air and electricity 🇫🇮
Doccla raised €5M to provide virtual wards, taking patients out of hospitals and monitoring them remotely 🇬🇧
Linio Biotech raised €4.2M to further develop its injectable cell-free product for skin healing and regeneration 🇫🇮
Phare Health closed a £2.5M Seed Round for their AI solution to help hospitals better understand their financial situation 🇬🇧
Floreon raised £2M to advance the production of their plant-based plastic, derived from crops as an alternative to oil-based plastics 🇬🇧
Bioxodes raised €12M (including a €3.4M public grant) to develop innovative therapies against thrombotic and inflammatory diseases 🇧🇪
Biomel raised £5.5M to commercially expand their suite of plant-based probiotics products for gut health 🇬🇧
Callyope raised €2.2M for their mental health monitoring platform that used speech to analyze brain functionality 🇫🇷
Biped.ai closed a CHF 1.2M round to develop a smart harness, worn on shoulders, that helps the visually impaired detect obstacles 🇨🇭
If you enjoyed this issue, share it with a friend or two
More from us
10 steps to join the startup world
A workbook to help you find your ideal role in the startup ecosystem.
From understanding the key players to finding hidden opportunities, this framework will guide you every step of the way.How to build startup teams
The ultimate guide on hiring, onboarding and retaining talent.
Learn the proven playbooks that have helped 100+ founders build winning teams. And if you’re looking to join a startup, this is your chance to learn everything that happens behind the curtains.Land your dream job with 1:1 private career coaching
Get actionable and tailored advice from someone who has overcome similar obstacles and doubts in their career.
You can book a 60-minute session by donating to any charity.